







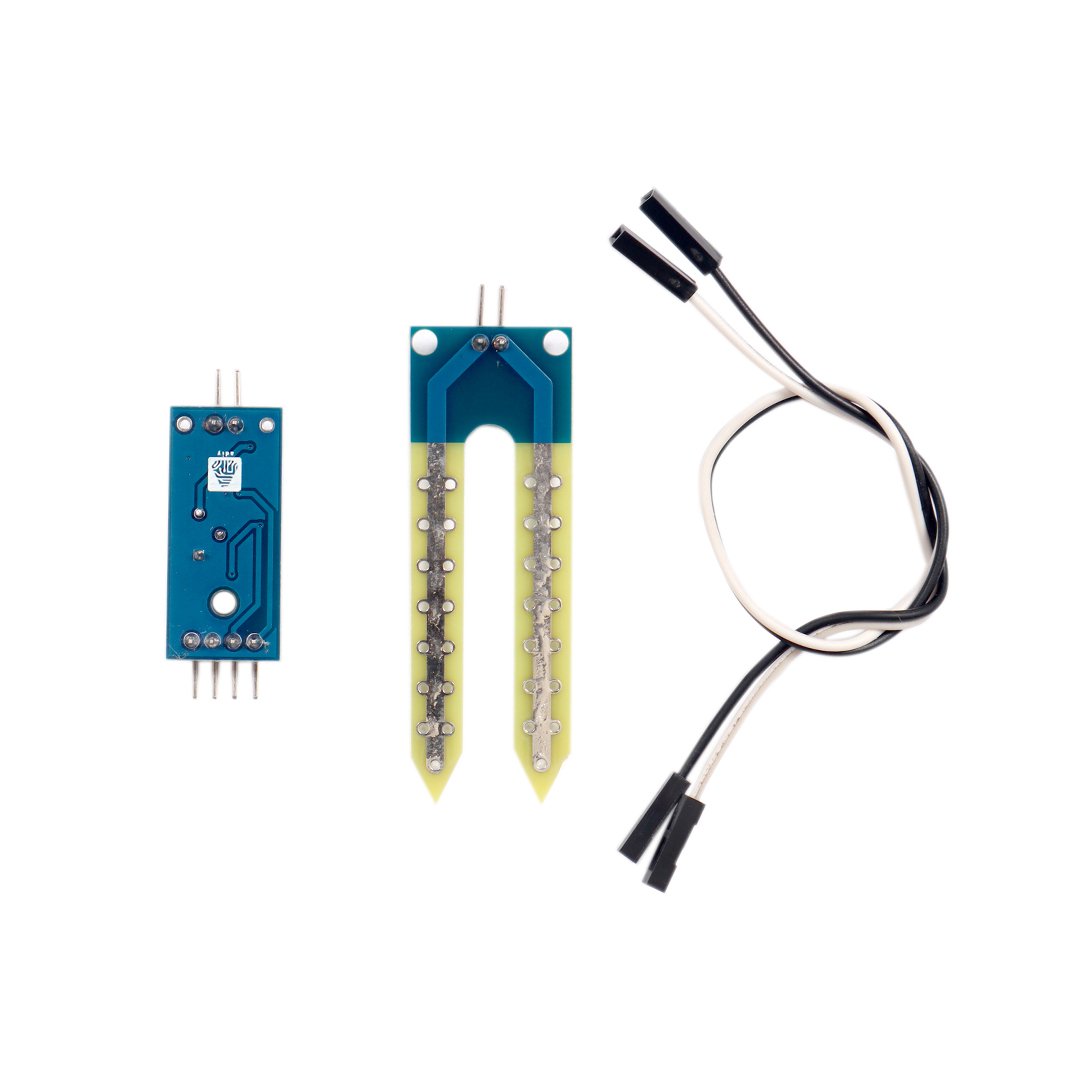
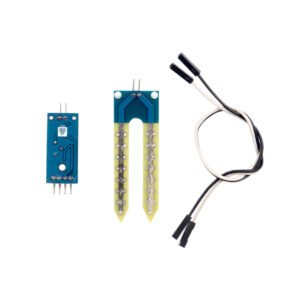
Soil Moisture Sensor
₹75.00 Original price was: ₹75.00.₹35.00Current price is: ₹35.00. (Including GST)
A soil moisture sensor, as its name implies, is an appliance for monitoring the moisture levels in the soil. Integrating this tool into the irrigation system may allow for more precise watering scheduling than is possible with past information or weather forecasts.
Specifications: Soil Moisture Sensor
- Dual output mode, analog output more accurate
- A fixed bolt hole for easy installation
- With power indicator (red) and digital switching output indicator (green)
- Having LM393 comparator chip, stable.
- Operating Voltage: 3.3V~5V
Description
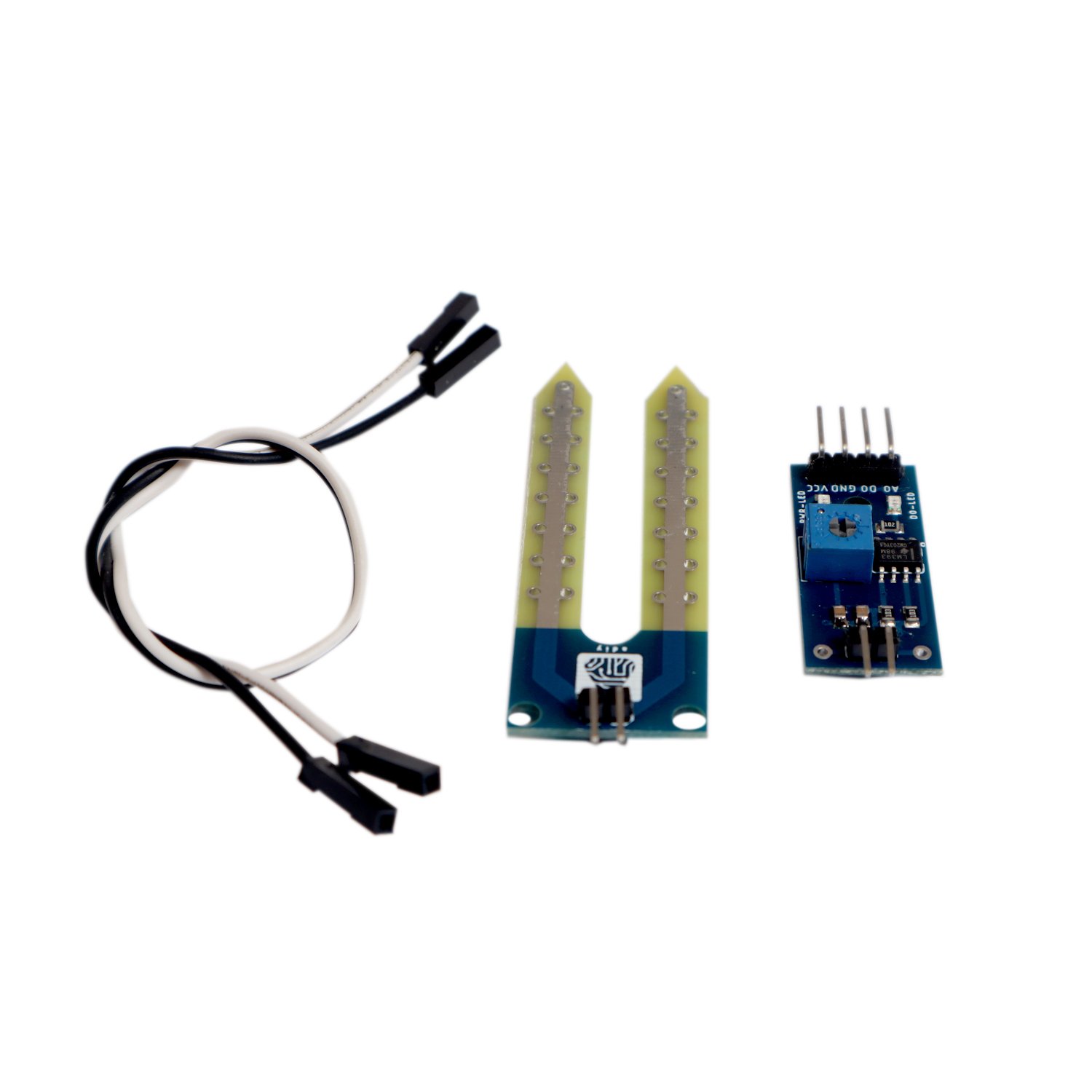
The Soil Moisture Sensor is a simple breakout for measuring the moisture in the soil and similar materials. The soil moisture sensor is pretty straightforward to use. The two large, exposed pads function as probes for the sensor, together acting as a variable resistor. The more water that is in the soil means the better the conductivity between the pads will be and will result in lower resistance, and a higher SIG out.
To get the Soil Moisture Sensor functioning all you will need is to connect the VCC and GND pins to your Arduino-based device (or compatible development board) and you will receive a SIG out which will depend on the amount of water in the soil.
Features: Soil Moisture Sensor
- Simple to use
- Passive component
- Resistive Sensor
Specifications: Soil Moisture Sensor
- Operating voltage: 3.3V~5V
- Dual output mode, analog output more accurate
- A fixed bolt hole for easy installation
- With power indicator (red) and digital switching output indicator (green)
- Having LM393 comparator chip, stable
- Panel PCB Dimension: Approx.3cm x 1.5cm
- Soil Probe Dimension: Approx. 6cm x 3cm
- Cable Length: Approx.21cm
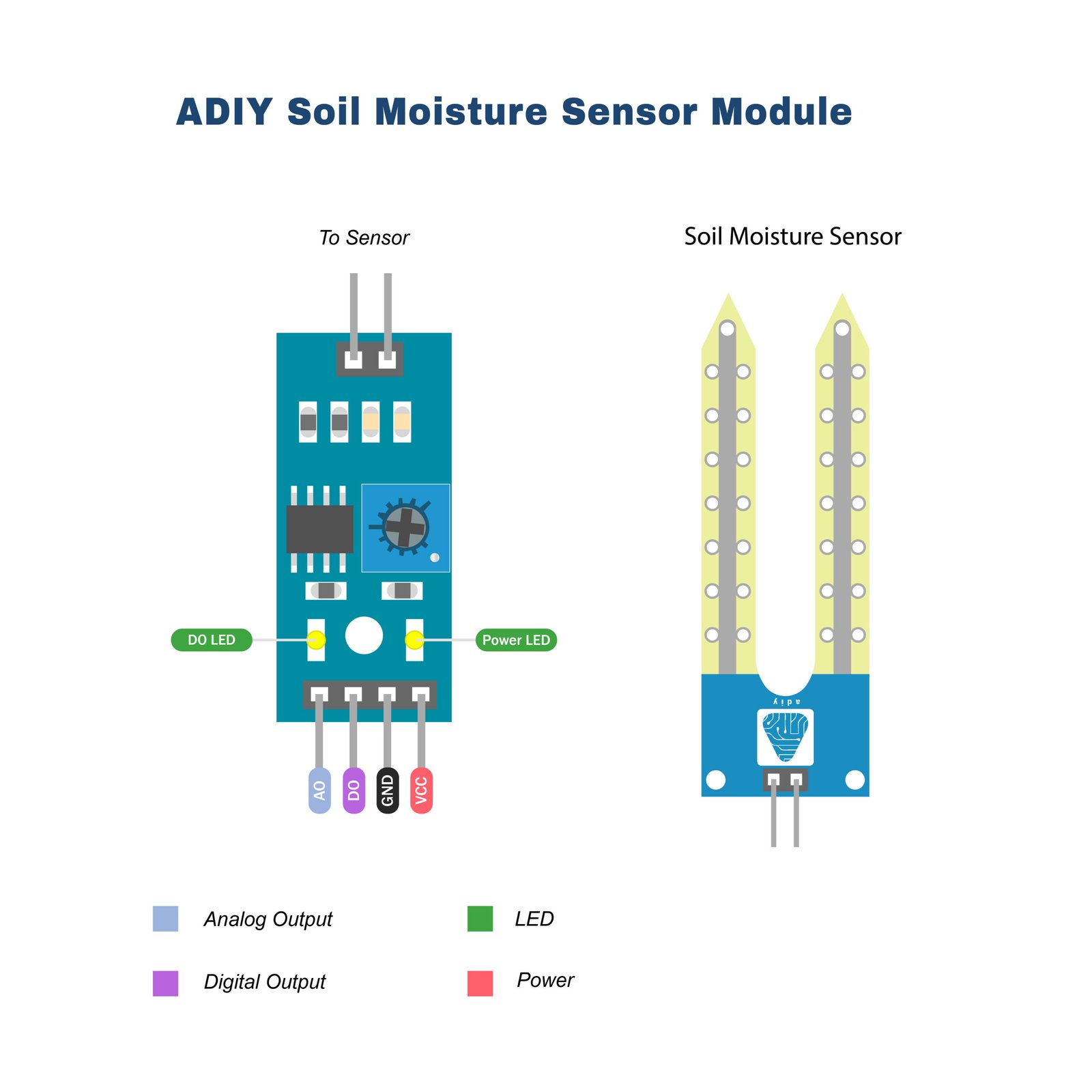
- VCC: 3.3V-5V
- GND: GND
- DO: digital output interface(0 and 1)
- AO: analog output interface
Package Includes: Soil Moisture Sensor
Resources – Usage Guide
……………………………………………………………………………………
How Does a Soil Moisture Sensor Work?
The soil moisture sensor operates in a straightforward manner.
The fork-shaped probe with two exposed conductors acts as a variable resistor (similar to a potentiometer) whose resistance varies with the soil’s moisture content.
This resistance varies inversely with soil moisture:
- The more water in the soil, the better the conductivity and the lower the resistance.
- The less water in the soil, the lower the conductivity and thus the higher the resistance.
The sensor produces an output voltage according to the resistance, which by measuring we can determine the soil moisture level.









Reviews
There are no reviews yet.